Oral Hygiene
WHAT IS GOOD ORAL HYGIENE?
Oral care is the practice of keeping your mouth clean and healthy. Good oral hygiene is necessary for the prevention of dental caries, periodontal diseases, halitosis and your other dental problem.
IMPORTANCE OF GOOD DENTAL HYGIENE.
Prevention is always better than cure. Good oral hygiene habits will keep you away from most of the dental problems saving you from toothaches and costly dental treatments. Modern dietary lifestyle habits are posing a greater risk for oral health.
MAINTAINING GOOD DENTAL HYGIENE,
WE CAN PREVENT.
Dental caries.
is a bacterial disease of calcified tissues of your teeth and is characterized by demineralization of the organic substance of the teeth.
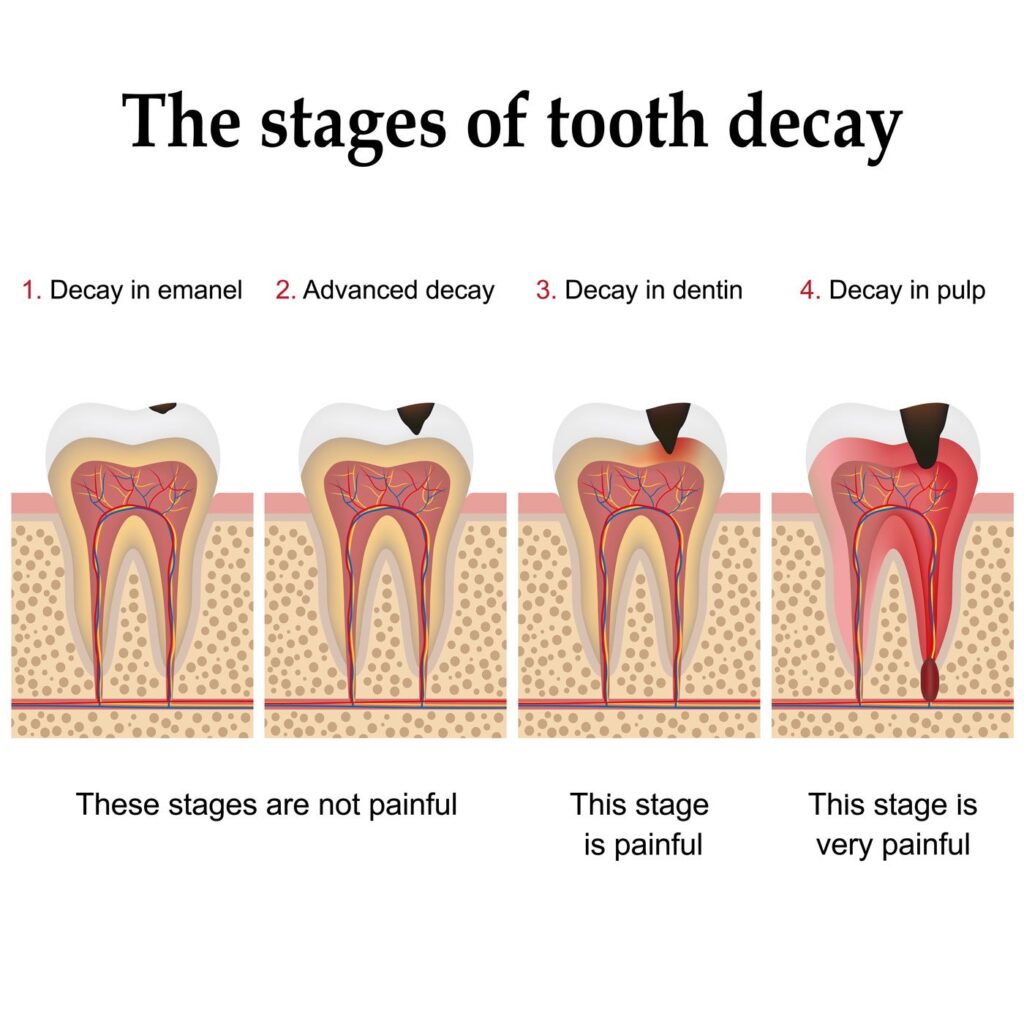
Dental cavities, more commonly known as tooth decay, are caused by a breakdown of your tooth enamel. This breakdown is the result of bacteria on teeth that break down foods and produce acid that destroys tooth enamel and results in tooth decay.
Dental caries can be reduced by maintaining proper and good oral hygiene, through brushing, flossing of your teeth etc.
Gingivitis or gum infection.
The inflammation of your gums or gingiva. It commonly occurs because a film of plaque, or bacteria, accumulates on your teeth. Gum infection is a non-destructive type of periodontal disease, but untreated gingivitis can progress to periodontitis. This is more serious and can eventually lead to loss of teeth.

Signs of gingivitis include red and puffy gums, that bleed easily when you brush your teeth. Gingivitis often resolves with good oral hygiene, such as longer and more frequent brushing, and flossing.
Periodontitis.
is a serious gum infection that damages your soft tissue and, without treatment, can destroy the bone that supports your teeth. Periodontitis can cause teeth to loosen or lead to tooth loss. Healthy gums are firm and pale pink and fit snugly around your teeth.
- Signs and symptoms include:
- Swollen or puffy gums.
- Bright red, dusky red or purplish gums.
- Gums that feel tender when touched.
- Gums that bleed easily.
- Pink tinged toothbrush after brushing.
- Spitting out blood when brushing or flossing your teeth.
- Pus between your teeth and gums.
- Bad breath or halitosis.
- Loose teeth or loss of teeth.
- Painful chewing.
- Gums that pull away from your teeth, making your teeth look longer than normal.
Periodontitis is common but largely preventable. It’s usually the result of poor oral hygiene. Brushing at least twice a day, flossing daily and getting regular dental checkups can greatly improve your chances of successful treatment for periodontitis.
Halitosis.
Bad breath or halitosis can result from your poor dental health habits and may be a sign of other health problems. Bad breath can also be made worse by the types of foods you eat and other unhealthy lifestyle habits
Food items that cause bad breath:

- Garlic.
- Onion.
- Cheese.
- Pastrami.
- Certain spices.
- Orange juice or soda.
- Alcohol.
Poor habits cause bad breath, if you don’t brush and floss teeth daily, food particles can remain in your mouth, promoting bacterial growth between teeth, around the gums, and on the tongue. Inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) from poor dental hygiene can also cause bad breath.
Odour-causing bacteria and food particles can cause bad breath if your dentures are not properly cleaned. Smoking or chewing tobacco-based products also can cause bad breath, stain teeth, reduce your ability to taste foods, and irritate your gums.
ORAL HYGIENE AIDS.

- Toothbrushes.
- Dental flosses.
- Interdental cleaners.
- Mouth rinses.
- Oral irrigators.
- Rubber tip stimulators.
- Tongue cleaners.
BRUSHING TECHNIQUES
Brushing your teeth is an important part of your oral care routine.

- Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristle brush. The size and shape of your brush should fit your mouth allowing you to reach all areas easily.
- Replace your toothbrush every three or four months, or sooner if the bristles are frayed. A worn toothbrush won’t do its job of cleaning your teeth.
- Use ADA-accepted fluoride toothpaste.
The proper brushing technique is to:
- Place your toothbrush at a 45-degree angle. Bristles should contact both the tooth surface and the gums.
- Gently brush the outer tooth surfaces of 2-3 teeth using a vibrating back, forth and rolling motion. Move brush to the next group of 2-3 teeth and repeat.
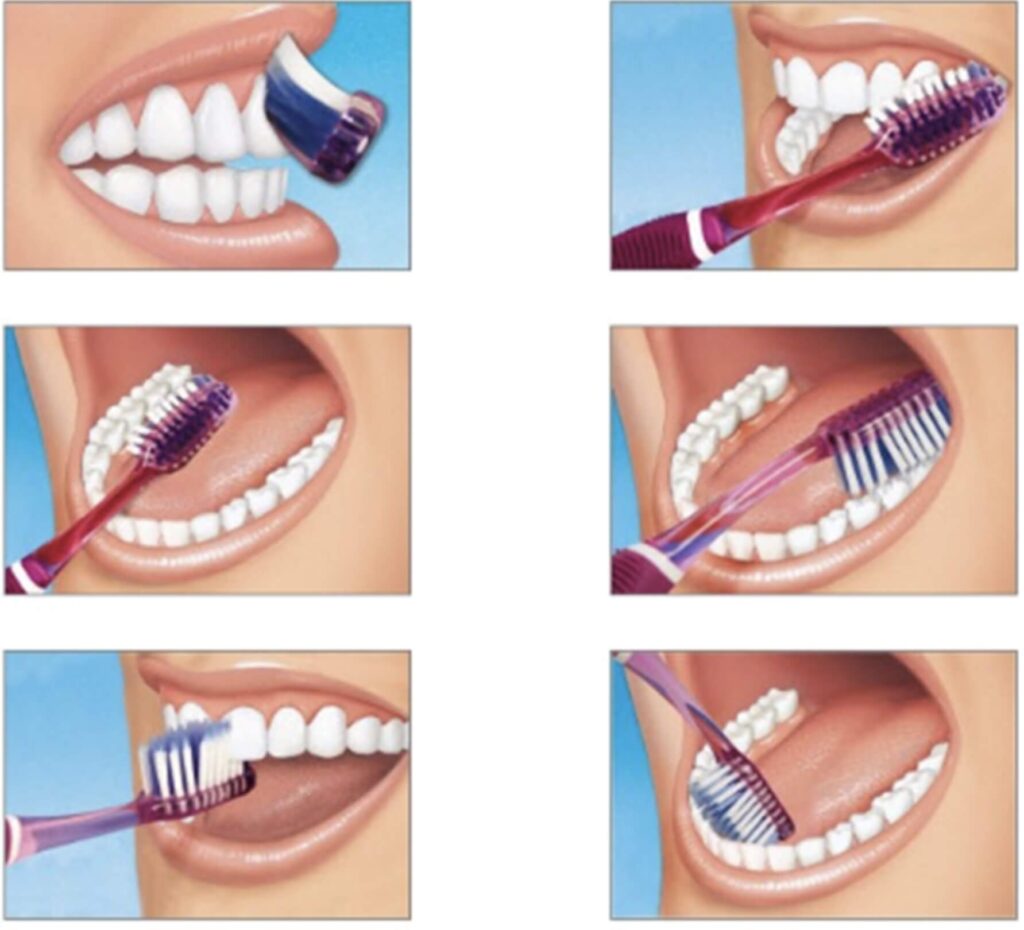
- Maintain a 45-degree angle with bristles contacting your tooth surface and gum line. Gently brush using back, forth and rolling motion along all of the inner tooth surfaces.
- Tilt brush vertically behind your front teeth. Make several up and down strokes using the front half of the brush.
- Place the brush against the biting surface of the teeth and use a gentle back and forth scrubbing motion. Brush the tongue from back to front to remove odour-producing bacteria.
FLOSSING
Flossing removes plaque from behind your teeth that brushing misses. It helps prevent periodontal disease by removing plaque.
Method:
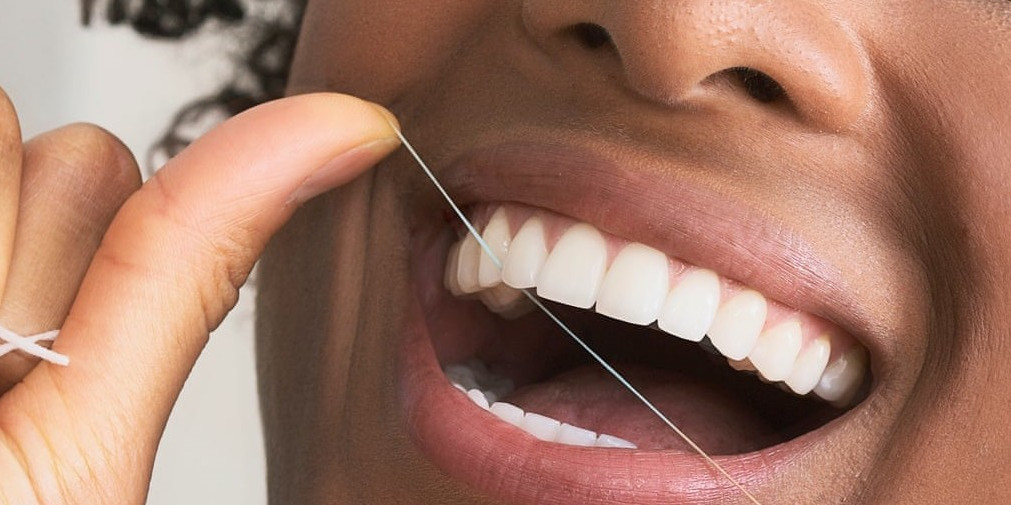
- Use an arms-length (18 inches) of floss. Wrap around your fingers mostly to one side.
- From each tooth forming a “c” shape with the floss each time.
- A new area of flossing needed to introduce for each gingival pocket.
- Do not forget to floss behind your last molar.
PROPER DIET
- Avoid foods that are high in sugar content.
- Carbonated drinks are more acidic than non-carbonated drinks; hence more dangerous.
- Food like potato crisps tends to stick in the grooves of your teeth, stay for an extended period and cause decay.
- Avoid excessive intake of fruits juices. They can be diluted with water.
OTHER INTERDENTAL CLEANERS
Oral Irrigation Devices Oral irrigators
clean nonadherent debris and bacteria around orthodontic appliances or any inaccessible areas. several types of oral irrigators are available depending upon irrigation pressure, water stream characteristics and jet type design.
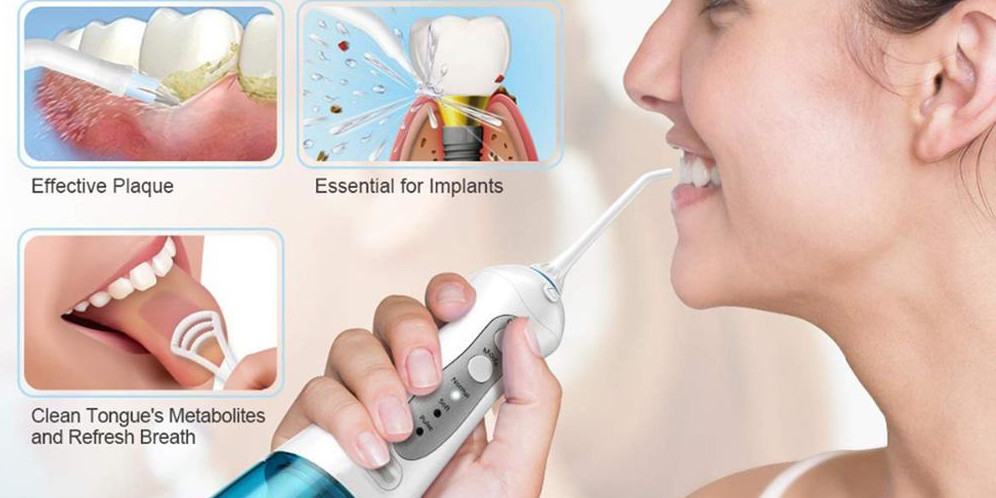
Syringe: A syringe can also be used for delivering a solution to irrigate the pocket.
Pulsating monojet irrigators: These are preferred for supragingival irrigation, e.g., Waterpik.
Multistreaming irrigators: These are available for supragingival irrigation.
Indications:
Patients undergoing orthodontic therapy: When other oral hygiene aids fail due to the presence of local factors, such as orthodontic appliances or intermaxillary fixation. Patients with: • Crown and bridgework. • Implants. • Surgical indication but unable to undergo surgery because of medical, behavioural or financial constraints.
Contraindications:
In infective endocarditis, patient irrigation may cause bacteremias. Hence, the method is not suitable in high-risk patients.
SINGLE TUFTED BRUSHES
One large bristle for cleaning spaces between teeth to carry medicated gel into pockets.
INTERDENTAL BRUSHES
- For cleaning pontics.
- For cleaning space between teeth

INTERDENTAL WOODSTICKS
- Specially shaped toothpicks are made from either wood or plastic.
- Used for interdental cleaning.
SUPER FLOSS
A special type of floss designed to clean beneath pontics or fixed bridges.
RINSING
- Regular rinses with a good mouthwash help to keep your mouth clean, fresh and germ-free.
- Daily rinses must be alcohol-free (they cause dryness of oral mucosa).
- Fluoride rinses help to boost the strength of newly erupted teeth.
REGULAR DENTAL CHECKUPS
Good oral hygiene should be a joint effort between you and your dentist.
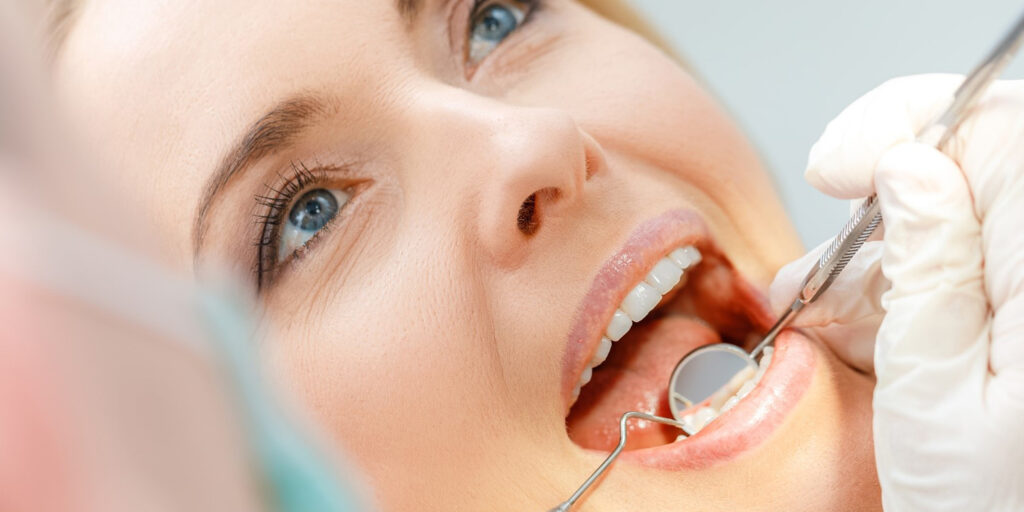
Your dentist, if visited regularly, will detect and prevent any problem before it becomes hazardous for you.
Regular dental checkups are an essential part of the dental hygiene routine for young and old alike
SIGNS OF GOOD ORAL HYGIENE
Good oral hygiene results in a mouth that looks and smells healthy.
It means:
- Your teeth are clean and free of debris.
- Gums are pink and do not hurt or bleed when you brush or floss.
- Bad breath or halitosis is not a constant problem.
FULL BODY CONNECTION WITH ORAL HYGIENE
Bacteria that cause periodontal disease can be spread through close contact between people

Approx. 90% of systemic diseases have a link to oral health.
People who have periodontal disease even more risk to have a fatal heart attack.
Infection in the mouth increases even more risk for respiratory infection.
Diabetes with periodontal diseases has more difficulty controlling blood sugar levels in contrast with healthy gums.
HOW TO MAINTAIN GOOD ORAL HYGIENE WITH BRACES?
Oral hygiene shouldn’t change with or without braces,brushing, flossing and visiting the dentist are all important during your treatment. You will just need to use a different technique to brush and floss with braces.
How many times a day to brush with braces?
- Should brush your teeth after every main meal and before bed.
- Brush your teeth any time that you have sugars in your food, so three to four times per day.
- It takes a little longer time to brush your teeth with braces.
Brushing with braces.
- You can use a manual likewise electric toothbrush.
- If not possible to brush after lunch or a snack rinse your mouth thoroughly with water to remove any food particles that have collected around the brackets and wire.
- If you won’t brush plaque builds up around the brackets and gum line. Its plaque causes staining on teeth when the braces are removed. Plaque also causes cavities and leads to gum infections.
- Use a fluoride gel or toothpaste to brush your teeth.
Flossing with braces.
- Is an essential part for your of good oral hygiene.
- Flossing is the only way to clean between your teeth and along the gum line.
- Take about 20cm of floss and wrap it around your index fingers. Thread the floss between the wire and the teeth. Using firm pressure, gently move the floss between the teeth and into the gum to remove plaque and food particles.
HOW TO MAINTAIN GOOD ORAL HYGIENE WITH A CLEAR ALIGNER?
- It’s easy to maintain oral hygiene with a clear aligner because it can be removed while having your food.
- Taking care of your teeth and practising good oral hygiene during clear aligner treatment will give you beautiful results and a healthy smile.
How to care, your invisible aligner?
Clear aligners are used to straighten teeth, they must be very tight-fitting and will develop a film on both the inside and outside surface.
They should be cleaned several times a day to prevent yellowing and odour.
How to clean your clear aligner?

- Brush the trays whenever you brush your teeth.
- Wash them with clear antibacterial hand soap and rinse thoroughly as needed.
- Always clean, or at least rinse, your aligners before storing them in case.
- Soak your aligners once daily in denture cleaner or aligner cleaning crystals.
- Above all replace your aligner with freshly brushed and flossed teeth.
Daily habits for maintaining good oral hygiene with clear aligner therapy.

- Brush and floss after eating meals and snacks or drinking anything other than water.
- Avoid hot drinks that cause stains, such as coffee and black tea.
- Floss picks or small dental floss to remove food stuck between teeth.
- Orthodontic wax to cover any uncomfortable edges.
- Aligner chewies, which help seat tray properly and can relieve discomfort.
- Aligner retrieval tools, which can help remove and replace the aligner
- Cleansing products,sprays,or towelette wipes, will allow to spray or wipe down while rinsing not practical.
- Hence a discreet case is essential to keep your aligner.
Thank You
http://pristinealigner.com


